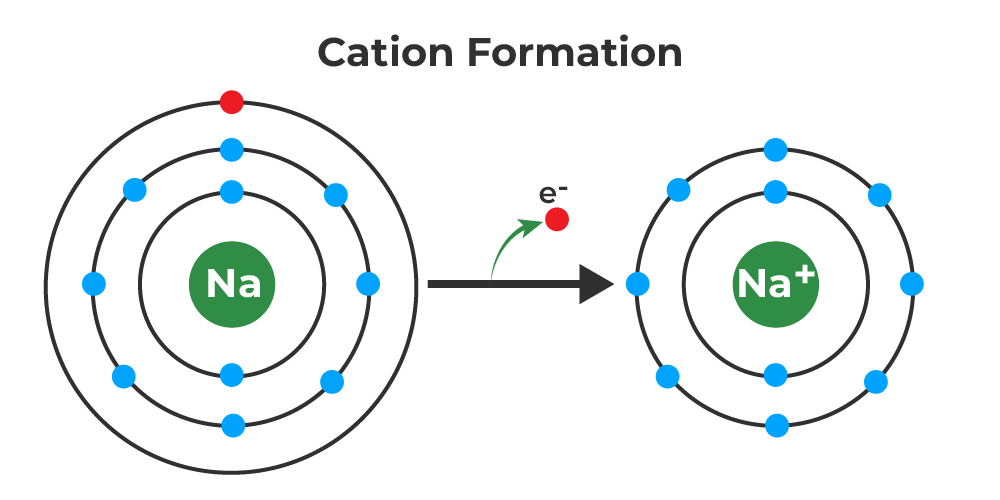
How Is A Cation Formed
How Is A Cation Formed - Determine the charges achieved when. Web a cation (a positive ion) forms when a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative. Groups 1 and 2 elements form cations. Web learn how cations and anions are formed by losing or gaining electrons, and how they are written in chemical. Web cations are formed by the loss of one or two electrons from an element. Web during the formation of some compounds, atoms gain or lose electrons, and form electrically charged particles. Explain how neutral atoms ionize to form cations. Web learn how cations are formed by the loss of one or more electrons from atoms. See examples of cation formation for alkali.
Cations and Anions Definitions, Examples, and Differences
Web cations are formed by the loss of one or two electrons from an element. Web learn how cations are formed by the loss of one or more electrons from atoms. Web a cation (a positive ion) forms when a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative. See examples of cation.
PPT ChemCatalyst PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5516040
Determine the charges achieved when. Web learn how cations are formed by the loss of one or more electrons from atoms. Groups 1 and 2 elements form cations. Explain how neutral atoms ionize to form cations. Web learn how cations and anions are formed by losing or gaining electrons, and how they are written in chemical.
PPT Ions and Ionic Compound PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3011004
Web a cation (a positive ion) forms when a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative. Web cations are formed by the loss of one or two electrons from an element. Web during the formation of some compounds, atoms gain or lose electrons, and form electrically charged particles. Groups 1 and.
Cations and Anions Difference between Cations and Anions
Groups 1 and 2 elements form cations. Web a cation (a positive ion) forms when a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative. See examples of cation formation for alkali. Web cations are formed by the loss of one or two electrons from an element. Web during the formation of some.
The Difference Between a Cation and an Anion
Web a cation (a positive ion) forms when a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative. Determine the charges achieved when. Web learn how cations are formed by the loss of one or more electrons from atoms. Web learn how cations and anions are formed by losing or gaining electrons, and.
Ions Meaning and Examples [in Chemistry] Teachoo Concepts
Web during the formation of some compounds, atoms gain or lose electrons, and form electrically charged particles. Determine the charges achieved when. Web a cation (a positive ion) forms when a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative. Web cations are formed by the loss of one or two electrons from.
Cation Ap Chemistry, Protons, Anatomy And Physiology, Sodium, Physics, Diagram, Positivity
See examples of cation formation for alkali. Explain how neutral atoms ionize to form cations. Web learn how cations are formed by the loss of one or more electrons from atoms. Web cations are formed by the loss of one or two electrons from an element. Web learn how cations and anions are formed by losing or gaining electrons, and.
Naming Ionic Compounds Chemistry Steps
Web a cation (a positive ion) forms when a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative. Web learn how cations and anions are formed by losing or gaining electrons, and how they are written in chemical. Web during the formation of some compounds, atoms gain or lose electrons, and form electrically.
PPT Ionic Bonding PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2664362
Web learn how cations and anions are formed by losing or gaining electrons, and how they are written in chemical. Web cations are formed by the loss of one or two electrons from an element. See examples of cation formation for alkali. Explain how neutral atoms ionize to form cations. Web during the formation of some compounds, atoms gain or.
Cations vs Anions Difference Between Cations and Anions with Examples
Web cations are formed by the loss of one or two electrons from an element. Web during the formation of some compounds, atoms gain or lose electrons, and form electrically charged particles. Explain how neutral atoms ionize to form cations. Groups 1 and 2 elements form cations. See examples of cation formation for alkali.
See examples of cation formation for alkali. Determine the charges achieved when. Groups 1 and 2 elements form cations. Web learn how cations and anions are formed by losing or gaining electrons, and how they are written in chemical. Web learn how cations are formed by the loss of one or more electrons from atoms. Explain how neutral atoms ionize to form cations. Web cations are formed by the loss of one or two electrons from an element. Web a cation (a positive ion) forms when a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative. Web during the formation of some compounds, atoms gain or lose electrons, and form electrically charged particles.
Determine The Charges Achieved When.
Web learn how cations and anions are formed by losing or gaining electrons, and how they are written in chemical. Web a cation (a positive ion) forms when a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative. See examples of cation formation for alkali. Web cations are formed by the loss of one or two electrons from an element.
Groups 1 And 2 Elements Form Cations.
Web during the formation of some compounds, atoms gain or lose electrons, and form electrically charged particles. Web learn how cations are formed by the loss of one or more electrons from atoms. Explain how neutral atoms ionize to form cations.





/cation-and-an-anion-differences-606111-v2_preview-5b44daf9c9e77c0037679d52.png)
![Ions Meaning and Examples [in Chemistry] Teachoo Concepts](https://i2.wp.com/d1avenlh0i1xmr.cloudfront.net/eb2b7929-97cd-4d38-9a03-b15e74a5e461/generation-of-cation-01.jpg)