Igneous Rocks Form Below Earth's Surface
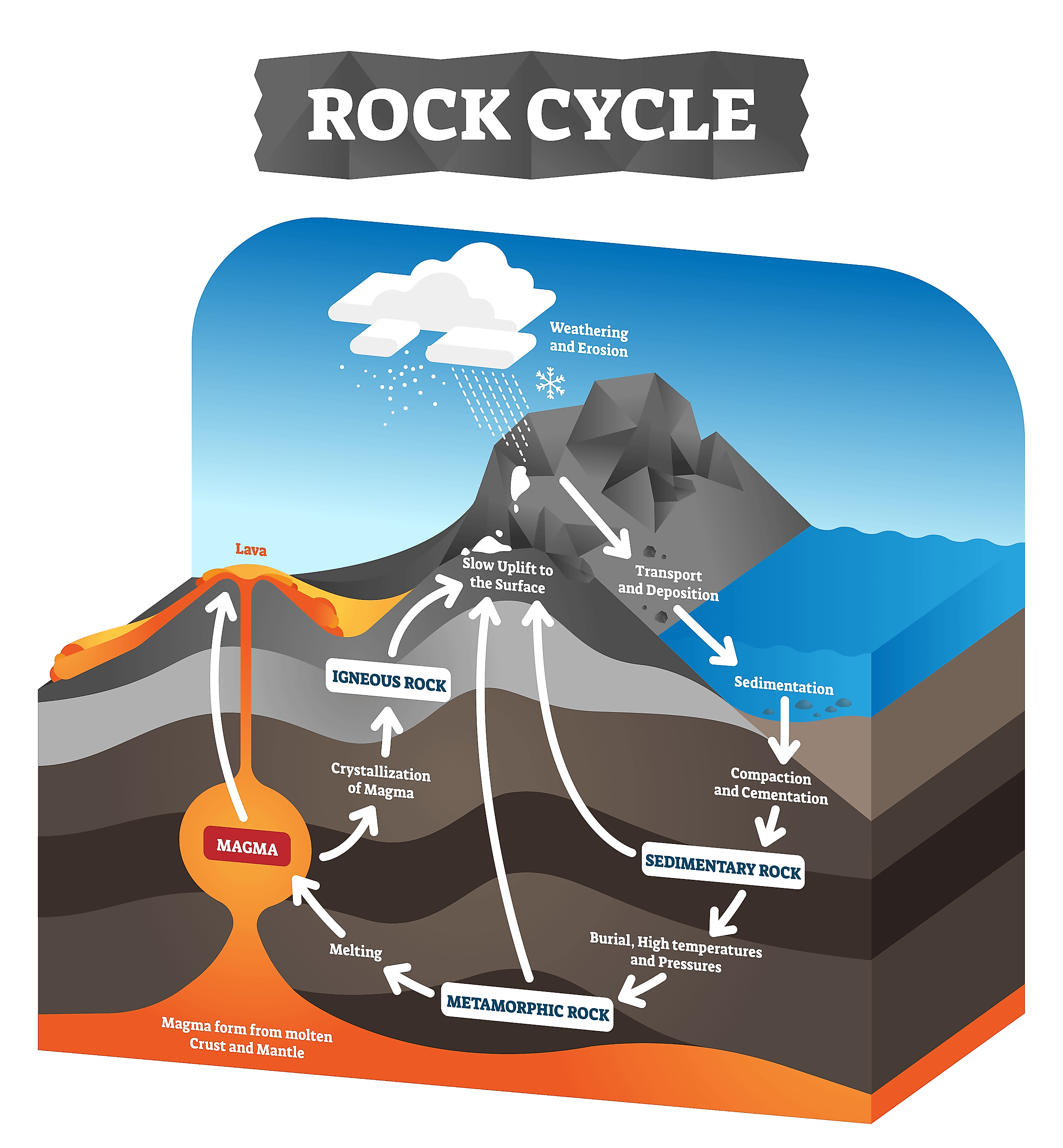
Igneous Rocks Form Below Earth's Surface - Web igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten. Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the. Web intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's surface, and the slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. Web plutonic or intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath the earth’s surface, leading to the. Web extrusive, or volcanic, igneous rock is produced when magma exits and cools above (or very near) the earth's surface. These are the rocks that form at. Web when rocks are pushed deep below earth’s surface, they can melt to form magma. Magma that reaches earth’s surface.
5.1.1 How do rocks form? Earth & Space Science
Web plutonic or intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath the earth’s surface, leading to the. Web when rocks are pushed deep below earth’s surface, they can melt to form magma. Web intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's surface, and the slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten.
PPT Chapter 3 2 Igneous Rocks! PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2581835
Web extrusive, or volcanic, igneous rock is produced when magma exits and cools above (or very near) the earth's surface. Web intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's surface, and the slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. Web plutonic or intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath the earth’s surface, leading to the. These are.
Igneous Rocks Definition, Types, Examples, & Pictures
Web igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten. Magma that reaches earth’s surface. Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the. Web intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's surface, and.
Igneous Rocks How Are They Formed? Universe Today
Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the. Magma that reaches earth’s surface. Web igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten. These are the rocks that form at. Web intrusive.
Igneous Rocks Formation, Classification, Examples, Uses Geology In
These are the rocks that form at. Magma that reaches earth’s surface. Web when rocks are pushed deep below earth’s surface, they can melt to form magma. Web igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten. Web extrusive, or volcanic, igneous rock.
How Are Igneous Rocks Formed? WorldAtlas
Magma that reaches earth’s surface. Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the. Web intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's surface, and the slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. Web when rocks are pushed deep below earth’s surface, they can melt to form magma. Web.
Igneous rocks form when molten rock cools and solidifies. Molten rock is called lava when it is
Web when rocks are pushed deep below earth’s surface, they can melt to form magma. Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the. Web extrusive, or volcanic, igneous rock is produced when magma exits and cools above (or very near) the earth's surface. These are the rocks that form.
How Are Igneous Rocks Formed? WorldAtlas
Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the. Web igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten. Web extrusive, or volcanic, igneous rock is produced when magma exits and cools above.
Igneous Rocks Definition, Classification and Examples Geology News, Tutorials and Articles
Magma that reaches earth’s surface. Web plutonic or intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath the earth’s surface, leading to the. Web intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's surface, and the slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. Web when rocks are pushed deep below earth’s surface, they can melt to form magma. These are.
Igneous Rocks Everything You Need to Know
Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the. Web igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten. Web plutonic or intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath the earth’s.
These are the rocks that form at. Web intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's surface, and the slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the. Web extrusive, or volcanic, igneous rock is produced when magma exits and cools above (or very near) the earth's surface. Web igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten. Magma that reaches earth’s surface. Web plutonic or intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath the earth’s surface, leading to the. Web when rocks are pushed deep below earth’s surface, they can melt to form magma.
These Are The Rocks That Form At.
Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the. Web igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten. Web intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's surface, and the slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. Web plutonic or intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath the earth’s surface, leading to the.
Web When Rocks Are Pushed Deep Below Earth’s Surface, They Can Melt To Form Magma.
Web extrusive, or volcanic, igneous rock is produced when magma exits and cools above (or very near) the earth's surface. Magma that reaches earth’s surface.









/about-igneous-rocks-1438950_final_CORRECTED2FINAL-f8d738e151b9437caa256d21155d091f.png)