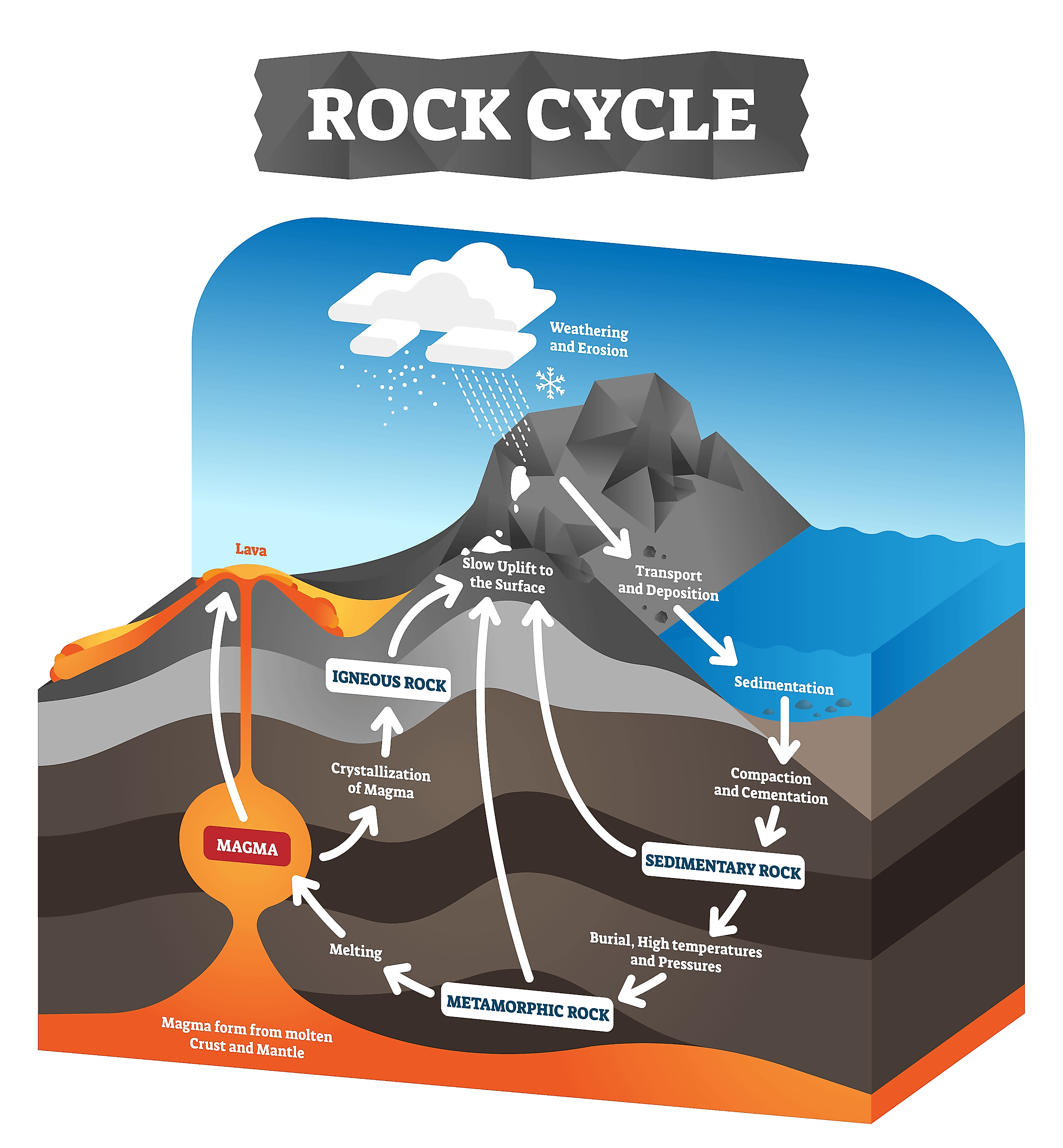
Igneous Rocks That Form Below Earth's Surface
Igneous Rocks That Form Below Earth's Surface - The slow cooling that occurs there allows large. Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the. Web batholith, large body of igneous rock formed beneath the earth’s surface by the intrusion and solidification of magma. Web intrusive igneous rocks that form near the surface are termed subvolcanic or hypabyssal rocks and they are usually. Web intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's surface, and the slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. Web plutonic or intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath the earth’s surface, leading to the. Web intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools and solidifies beneath the earth’s surface.
Igneous Rocks How Are They Formed? Universe Today
The slow cooling that occurs there allows large. Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the. Web plutonic or intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath the earth’s surface, leading to the. Web batholith, large body of igneous rock formed beneath the earth’s surface by the intrusion.
Igneous Rocks Definition, Classification and Examples Geology News, Tutorials and Articles
Web intrusive igneous rocks that form near the surface are termed subvolcanic or hypabyssal rocks and they are usually. Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the. The slow cooling that occurs there allows large. Web intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools and solidifies beneath the earth’s surface..
Igneous Rocks Everything You Need to Know
Web plutonic or intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath the earth’s surface, leading to the. Web batholith, large body of igneous rock formed beneath the earth’s surface by the intrusion and solidification of magma. Web intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's surface, and the slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. The slow cooling.
Geology Fundamentals Identifying Igneous Rocks in the Field Geology for Investors
Web intrusive igneous rocks that form near the surface are termed subvolcanic or hypabyssal rocks and they are usually. Web intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools and solidifies beneath the earth’s surface. Web plutonic or intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath the earth’s surface, leading to the. Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools.
Rocks Geography study Material & Notes
Web plutonic or intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath the earth’s surface, leading to the. Web batholith, large body of igneous rock formed beneath the earth’s surface by the intrusion and solidification of magma. Web intrusive igneous rocks that form near the surface are termed subvolcanic or hypabyssal rocks and they are usually. Web igneous rocks form.
How Are Igneous Rocks Formed? WorldAtlas
Web batholith, large body of igneous rock formed beneath the earth’s surface by the intrusion and solidification of magma. Web intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools and solidifies beneath the earth’s surface. The slow cooling that occurs there allows large. Web intrusive igneous rocks that form near the surface are termed subvolcanic or hypabyssal rocks and they are usually..
The Texture of Igneous Rocks Igneous rock, Igneous, Geology
Web intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools and solidifies beneath the earth’s surface. Web batholith, large body of igneous rock formed beneath the earth’s surface by the intrusion and solidification of magma. Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the. Web plutonic or intrusive igneous rocks form when.
The Relationship Between Igneous Rocks & Tectonic Plates Geology In Plate tectonics, Geology
Web batholith, large body of igneous rock formed beneath the earth’s surface by the intrusion and solidification of magma. Web intrusive igneous rocks that form near the surface are termed subvolcanic or hypabyssal rocks and they are usually. Web plutonic or intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath the earth’s surface, leading to the. Web intrusive igneous rocks.
Volcanism Understanding Global Change
Web plutonic or intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath the earth’s surface, leading to the. Web batholith, large body of igneous rock formed beneath the earth’s surface by the intrusion and solidification of magma. Web intrusive igneous rocks that form near the surface are termed subvolcanic or hypabyssal rocks and they are usually. Web intrusive igneous rocks.
Igneous Rocks Definition, Types, Examples, & Pictures
The slow cooling that occurs there allows large. Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the. Web intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's surface, and the slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. Web intrusive igneous rocks that form near the surface are termed subvolcanic or.
Web intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools and solidifies beneath the earth’s surface. Web plutonic or intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath the earth’s surface, leading to the. Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the. The slow cooling that occurs there allows large. Web batholith, large body of igneous rock formed beneath the earth’s surface by the intrusion and solidification of magma. Web intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's surface, and the slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. Web intrusive igneous rocks that form near the surface are termed subvolcanic or hypabyssal rocks and they are usually.
Web Batholith, Large Body Of Igneous Rock Formed Beneath The Earth’s Surface By The Intrusion And Solidification Of Magma.
Web intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools and solidifies beneath the earth’s surface. Web intrusive igneous rocks that form near the surface are termed subvolcanic or hypabyssal rocks and they are usually. Web intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's surface, and the slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the.
The Slow Cooling That Occurs There Allows Large.
Web plutonic or intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath the earth’s surface, leading to the.



/about-igneous-rocks-1438950_final_CORRECTED2FINAL-f8d738e151b9437caa256d21155d091f.png)